Acid Hydrolysis Of Methyl Butanoate
11.9: Hydrolysis of Esters
- Folio ID
- 288341
Learning Objectives
- Depict the typical reaction that takes identify with esters.
- Identify the products of an acidic hydrolysis of an ester.
- Identify the products of a basic hydrolysis of an ester.
Esters are neutral compounds, unlike the acids from which they are formed. In typical reactions, the alkoxy (OR′) group of an ester is replaced by some other grouping. Ane such reaction is hydrolysis, literally "splitting with water." The hydrolysis of esters is catalyzed by either an acid or a base.
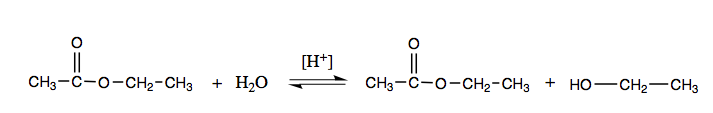
Acidic hydrolysis is only the reverse of esterification. The ester is heated with a large excess of water containing a strong-acid goad. Like esterification, the reaction is reversible and does not get to completion.
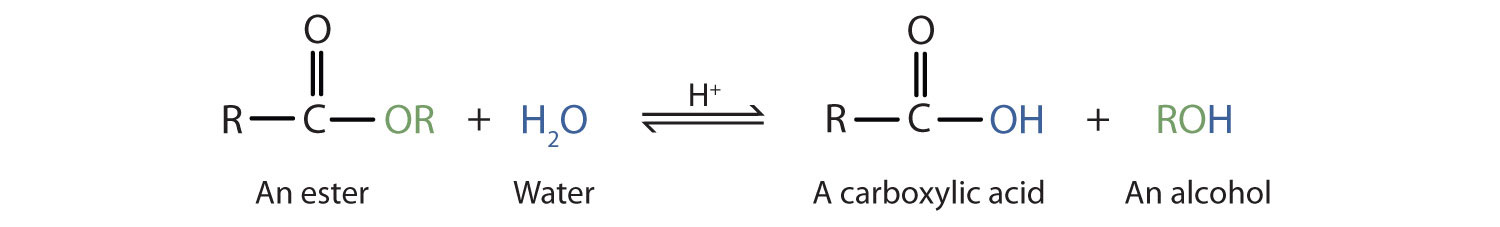
As a specific example, butyl butanoate and water react to form ethanoic acid and 1-butanol. The reaction is reversible and does not go to completion.

Case \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Write an equation for the acidic hydrolysis of ethyl butanoate,  , and proper noun the products.
, and proper noun the products.
Solution
Remember that in acidic hydrolysis, h2o (HOH) splits the ester bond. The H of HOH joins to the oxygen cantlet in the OR part of the original ester, and the OH of HOH joins to the carbonyl carbon cantlet:
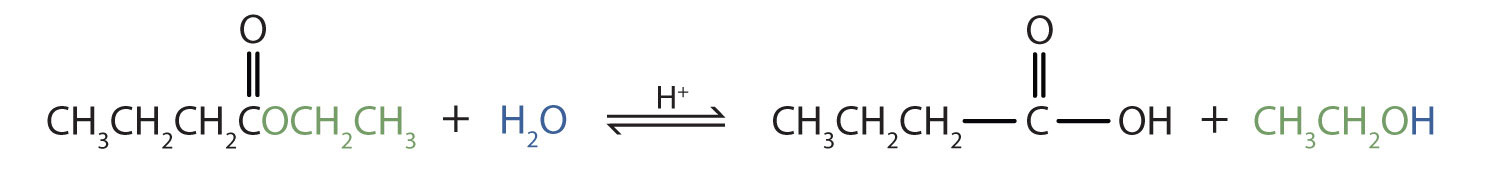
The products are butanoic acrid and ethanol.
Practise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Write an equation for the acidic hydrolysis of methyl butanoate and name the products.
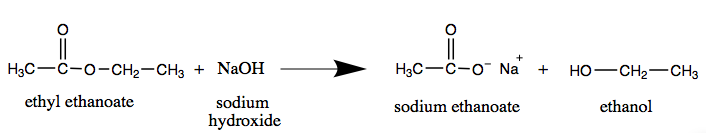
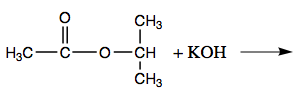
When a base (such equally sodium hydroxide [NaOH] or potassium hydroxide [KOH]) is used to hydrolyze an ester, the products are a carboxylate common salt and an alcohol. Because soaps are prepared by the alkaline hydrolysis of fats and oils, alkaline hydrolysis of esters is called saponification (Latin sapon, significant "soap," and facere, meaning "to make"). In a saponification reaction, the base is a reactant, non simply a catalyst. The reaction goes to completion:

Equally a specific example, ethyl acetate and NaOH react to form sodium acetate and ethanol:
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Write an equation for the hydrolysis of methyl benzoate in a potassium hydroxide solution.
Solution
In basic hydrolysis, the molecule of the base splits the ester linkage. The acid portion of the ester ends up as the salt of the acid (in this case, the potassium salt). The alcohol portion of the ester ends up as the free alcohol.

Exercise \(\PageIndex{ii}\)
Write the equation for the hydrolysis of ethyl propanoate in a sodium hydroxide solution.
Summary
Hydrolysis is a almost of import reaction of esters. Acidic hydrolysis of an ester gives a carboxylic acid and an booze. Bones hydrolysis of an ester gives a carboxylate salt and an booze.
Concept Review Exercises
-
How do acidic hydrolysis and bones hydrolysis of an ester differ in terms of the products obtained?
-
What is saponification?
Answers
-
acidic hydrolysis: carboxylic acid + alcohol; basic hydrolysis: carboxylate salt + alcohol
-
the bones hydrolysis of an ester
Exercises
-
Write an equation for the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of ethyl ethanoate.
-
Write an equation for the base of operations-catalyzed hydrolysis of ethyl ethanoate.
-
Consummate each equation.
-
-
Consummate each equation.
-
Answers
Acid Hydrolysis Of Methyl Butanoate,
Source: https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Fullerton_College/Introductory_Chemistry_for_Allied_Health_(Chan)/11%3A_Organic_Acids_and_Some_of_Their_Derivatives_Part_1/11.09%3A_Hydrolysis_of_Esters
Posted by: ramseybroolivies.blogspot.com


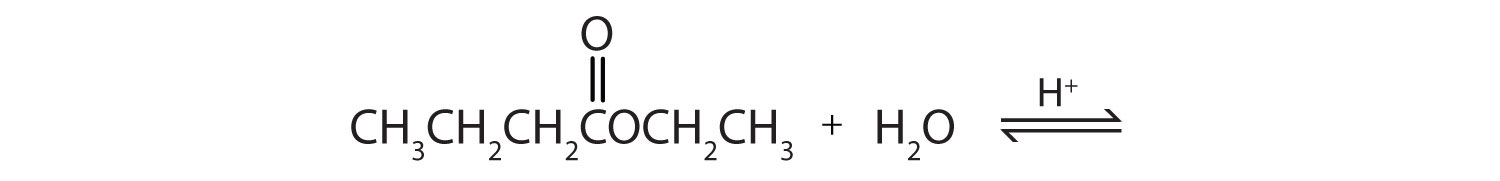


0 Response to "Acid Hydrolysis Of Methyl Butanoate"
Post a Comment